publications
2023
-
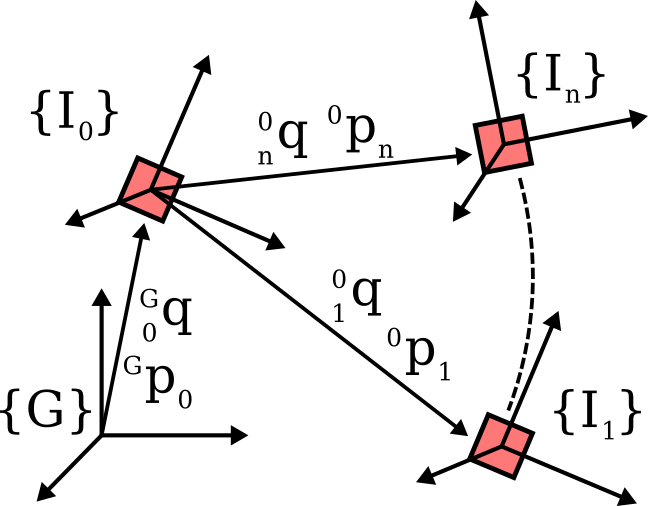 Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth Saripalli2023
Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth Saripalli2023Visual-inertial navigation systems are powerful in their ability to accurately estimate localization of mobile systems within complex environments that preclude the use of global navigation satellite systems. However, these navigation systems are reliant on accurate and up-to-date temporospatial calibrations of the sensors being used. As such, online estimators for these parameters are useful in resilient systems. This paper presents an extension to existing Kalman Filter based frameworks for estimating and calibrating the extrinsic parameters of multi-camera IMU systems. In addition to extending the filter framework to include multiple camera sensors, the measurement model was reformulated to make use of measurement data that is typically made available in fiducial detection software. A secondary filter layer was used to estimate time translation parameters without closed-loop feedback of sensor data. Experimental calibration results, including the use of cameras with non-overlapping fields of view, were used to validate the stability and accuracy of the filter formulation when compared to offline methods. Finally the generalized filter code has been open-sourced and is available online.
2022
-
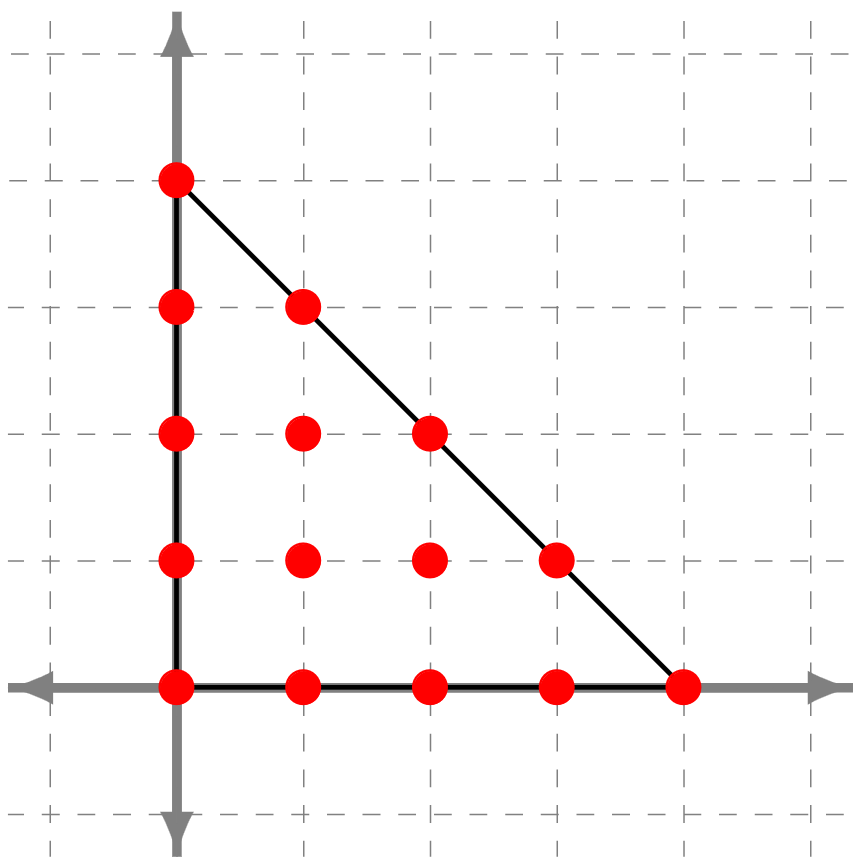 Jacob Hartzer, Olivia Röhrig, Timo de Wolff, and 1 more authorJournal of Symbolic Computation, 2022
Jacob Hartzer, Olivia Röhrig, Timo de Wolff, and 1 more authorJournal of Symbolic Computation, 2022Maximal mediated sets (MMS), introduced by Reznick, are distinguished subsets of lattice points in integral polytopes with even vertices. MMS of Newton polytopes of AGI-forms and nonnegative circuit polynomials determine whether these polynomials are sums of squares. In this article, we take initial steps in classifying MMS both theoretically and practically. Theoretically, we show that MMS of simplices are isomorphic if and only if the simplices generate the same lattice up to permutations. Furthermore, we generalize a result of Iliman and the third author. Practically, we fully characterize the MMS for all simplices of sufficiently small dimensions and maximal 1-norms. In particular, we experimentally prove a conjecture by Reznick for 2 dimensional simplices up to maximal 1-norm 150 and provide indications on the distribution of the density of MMS.
-
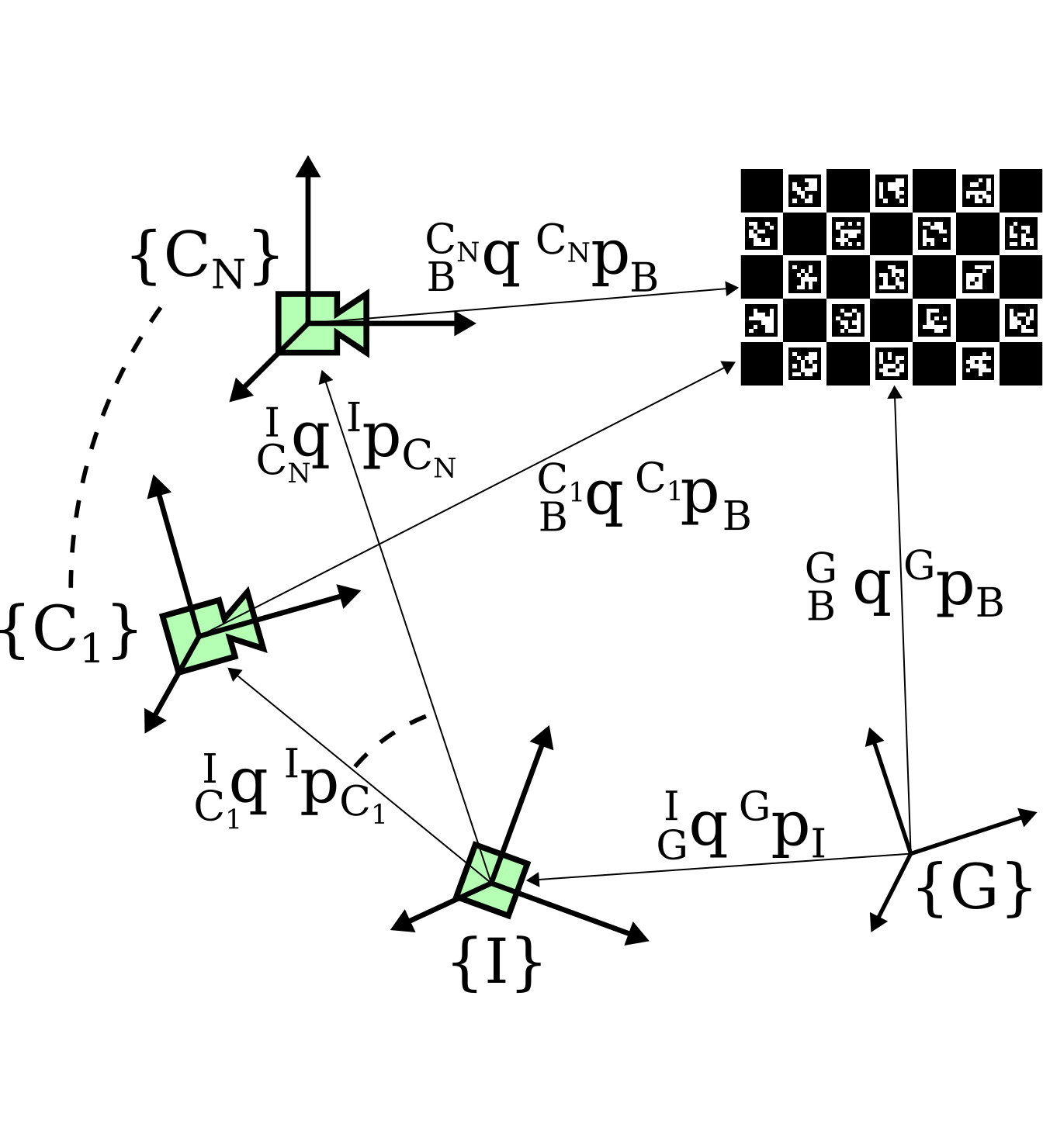 Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), 2022
Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), 2022This work presents a centralized multi-IMU filter framework with online intrinsic and extrinsic calibration for unsynchronized inertial measurement units that is robust against changes in calibration parameters. The novel EKF-based method estimates the positional and rotational offsets of the system of sensors as well as their intrinsic biases without the use of rigid body geometric constraints. Additionally, the filter is flexible in the total number of sensors used while leveraging the commonly used MSCKF framework for camera measurements. The filter framework has been validated using Monte Carlo simulation as well as experimentally. In both simulations and experiments, using multiple IMU measurement streams within the proposed filter framework outperforms the use of a single IMU in a filter prediction step while also producing consistent and accurate estimates of initial calibration errors. Compared to current state-of-the-art optimizers, the filter produces similar intrinsic and extrinsic calibration parameters for each sensor. Finally, an open source repository has been provided at this https URL containing both the online estimator and the simulation used for testing and evaluation.
2021
-
 Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), 2021
Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), 2021This paper develops a distributed collaborative localization algorithm based on an extended kalman filter. This algorithm incorporates Ultra-Wideband measurements for vehicle to vehicle ranging, and shows improvements in localization accuracy where GPS typically falls short. The algorithm was first tested in a newly created open-source simulation environment that emulates various numbers of vehicles and sensors while simultaneously testing multiple localization algorithms. Predicted error distributions for various algorithms are quickly producible using the Monte-Carlo method and optimization techniques within MatLab. The simulation results were validated experimentally in an outdoor, urban environment. Improvements of localization accuracy over a typical extended kalman filter ranged from 2.9% to 9.3% over 180 meter test runs. When GPS was denied, these improvements increased up to 83.3 % over a standard kalman filter. In both simulation and experimentally, the Decentralized Collaborative Localization algorithm was shown to be a good approximation of a full state filter, while reducing required communication between vehicles. These results are promising in showing the efficacy of adding UWB ranging sensors to cars for collaborative and landmark localization, especially in GPS-denied environments. In the future, additional moving vehicles with additional tags will be tested in other challenging GPS denied environments.
2020
-
 Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2020
Jacob Hartzer, and Srikanth SaripalliIn 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2020This paper summarizes the progress in developing a rugged, low-cost, automated ground cone robot network capable of traffic delineation at lane-level precision. A holonomic omnidirectional base with a traffic delineator was developed to allow flexibility in initialization. RTK GPS was utilized to reduce minimum position error to 2 centimeters. Due to recent developments, the cost of the platform is now less than $1,600. To minimize the effects of GPS-denied environments, wheel encoders and an Extended Kalman Filter were implemented to maintain lane-level accuracy during operation and a maximum error of 1.97 meters through 50 meters with little to no GPS signal. Future work includes increasing the operational speed of the platforms, incorporating lanelet information for path planning, and cross-platform estimation.
-
 Jacob HartzerTexas A&M University, 2020
Jacob HartzerTexas A&M University, 2020This thesis summarizes the development of a collaborative localization algorithm simulation environment and the implementation of collaborative localization using Ultra-Wideband ranging in autonomous vehicles. In the developed simulation environment, multi-vehicle scenarios are testable with various sensor combinations and configurations. The simulation emulates the networking required for collaborative localization and serves as a platform for evaluating algorithm performance using Monte Carlo analysis. Monte-Carlo simulations were run using a number of situations and vehicles to test the efficacy of UWB sensors in decentralized collaborative localization as well as landmark measurements within an extended Kalman filter. Improvements from adding Ultra-Wideband ranging were shown in all simulated environments, with landmarks offering additional improvements to collaborative localization, and with the most significant accuracy improvements seen in GNSS-denied environments. Physical experiments were run using a by-wire GEM e6 from Autonomous Stuff in an urban environment in both collaborative and landmark setups. Due to higher than expected INS certainty, adding UWB measurements showed smaller improvements than simulations. Improvements of 9.2 to 12.1% were shown through the introduction of Ultra-Wideband ranging measurements in a decentralized collaborative localization algorithm. Improvements of 30.6 to 83.3% were shown in using UWB ranging measurements to landmarks in an Extended Kalman Filter for street crossing and tunnel environments respectively. These results are similar to the simulated data, and are promising in showing the efficacy of adding UWB ranging sensors to cars for collaborative and landmark localization, especially in GNSS-denied environments. In the future, additional moving vehicles with additional tags will be tested and further evaluations of the UWB ranging modules will be performed.
2017
-
 Jacob Hartzer, and Christopher O’NeillINTEGERS , 2017
Jacob Hartzer, and Christopher O’NeillINTEGERS , 2017Arithmetical congruence monoids, which arise in non-unique factorization theory, are multiplicative monoids Ma,b consisting of all positive integers n satsfying the modular equation n ⌘ a mod b. In this paper, we examine the asymptotic behavior of the set of irreducible elements of Ma,b, and characterize in terms of a and b when this set forms an eventually periodic sequence.